gravimetric adsorption method definition|different types of gravimetric methods : importer When the signal is the mass of a precipitate, we call the method precipitation gravimetry. The indirect determination of PO3−3 PO 3 3 − by precipitating Hg 2 Cl 2 is an example, as is the direct determination of Cl – by . Acesse clarotvmais.com.br clique em Assine Já, faça login com sua conta do Minha Claro,acesse a página de PACOTES e escolha os pacotes de TV que quiser assinar. A cobrança virá na próxima fatura Claro. Caso não tenha login do Minha Claro é só clicar em AINDA NÃO POSSUI CONTA – CADASTRE-SE . O pagamento por cartão de crédito é .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Ache e baixe recursos grátis para Cerrado Brasil. 100.000+ vetores, fotos de arquivo e arquivos PSD. Grátis para uso comercial Imagens de alta qualidade.
There are differences and commonalities between gravimetric and volumetric experiments used to determine adsorption kinetics. We begin with some common features and discuss more specific differences in reference to the configurations used in commercial systems.

We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative determination of the amount of analyte through a precipitation process, precipitate isolation, and determination of isolated product weight. When the signal is the mass of a precipitate, we call the method precipitation gravimetry. The indirect determination of PO3−3 PO 3 3 − by precipitating Hg 2 Cl 2 is an example, as is the direct determination of Cl – by .Gravimetric Methods of Analysis [gravi – metric; weighing – measure] Hydrated and anhydrous copper sulfate [CuSO4 xH2O] Features of Gravimetric Analysis •A given analyte is isolated .
Adsorption: A process in which a substance (gas, liquid, or solid) is held on the surface of a solid. Absorption: A process in which a substance within the pores of a solid. •Attached directly .The change in the absorbent’s mass provides a direct determination of the amount of water in the sample. An easier approach is to weigh the sample of food before and after heating, using .
9/17/13. Student Learning Objectives. Your first unknown in lab will be a sample that contains chloride ion. You will analyze this sample by dissolving it in water and quantitatively .Gravimetric analysis, a method of quantitative chemical analysis in which the constituent sought is converted into a substance (of known composition) that can be separated from the sample and .
Gravimetric analysis describes a set of methods used in analytical chemistry for the quantitative determination of an analyte (the ion being analyzed) based on its mass.
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are porous crystalline materials that are promising for adsorption-based, on-board storage of hydrogen in fuel-cell vehicles. Volumetric and gravimetric hydrogen capacities are the key factors that determine the size and weight of the MOF-filled tank required to store a certain amount of hydrogen for reasonable driving range. . Using Mass as an Analytical Signal; Types of Gravimetric Methods; Conservation of Mass; Why Gravimetry is Important; Before we consider specific gravimetric methods, let’s take a moment to develop a broad survey of gravimetry.Later, as you read through the descriptions of specific gravimetric methods, this survey will help you focus on their . Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative method for accurately determining the amount of a substance by selective precipitation of the substance from an aqueous solution. The precipitate is separated from the remaining aqueous solution by filtration and is then weighed. Assuming that the chemical formula for the precipitate is known and that the .
Module 3 – Gravimetric Methods of Analysis. Definition of Terms. effective charge - can be thought of as a measure of the repulsive force the particle exerts on like particles in the solution.. signal - (in the context of chemical analysis) a detectable physical quantity or impulse by which information can be derived. analyte – a chemical substance that is the subject of chemical .MIDTERM: Gravimetric Methods of Analysis, so you can be ready for test day. . a drastic but effective way to minimize the effects of adsorption. AKA double precipitation. a process in which normally soluble compounds are carried out of solution by a precipitate. 3 of 60. Definition. . Choose matching definition.The gravimetric sorption technique is one of the most popular methods used to determine the amount and rate of the interaction of a gas or vapor with a material. The material can be a solid or liquid, and both thermodynamics and kinetics of the sorption process are recorded. Gravimetric Sorption Technique: Working PrincipleIn gravimetric analysis, which consists on precipitating the analyte and measuring its mass to determine its concentration or purity, coprecipitation is a problem because undesired impurities often coprecipitate with the analyte, resulting in excess mass. This problem can often be mitigated by "digestion" (waiting for the precipitate to .
Using Mass as an Analytical Signal; Types of Gravimetric Methods; Conservation of Mass; Why Gravimetry is Important; Before we consider specific gravimetric methods, let’s take a moment to develop a broad survey of gravimetry.Later, as you read through the descriptions of specific gravimetric methods, this survey will help you focus on their .Impurities encountered in Gravimetric Analysis • 3. Surface adsorption • Surface adsorption is very common especially in colloidal precipitates. • Example, AgCl, BaSO , where each of them will have a primary adsorption 4 layer of the lattice ion present in excess followed by a secondary layer of the counter ion of opposite charge.Adsorption: A process in which a substance (gas, liquid, or solid) is held on the surface of a solid. Absorption: A process in which a substance within the pores of a solid. •Attached directly to the solid surface is the primary adsorption layer, which consists mainly of adsorbed silver ions. Surrounding the charged particle is aThe manometric method is usually used to determine the adsorption diffusivity, as shown in Fig. 3 a [3,30,58–60].The experimental set-up generally consists of three parts: I. Gas supply system; II. Analysis system; III. Data acquisition system. Different from the system for the volumetric method, it needs a reference cell to determine how much gas is adsorbed during .
Precipitation and volatilization gravimetric methods require that the analyte, or some other species in the sample, participate in a chemical reaction. . Adsorption, absorption, and binding occur at the interface between the solution containing the analyte and the substrate’s surface, the thin film, or the receptor. Although the amount of . In precipitation gravimetry an insoluble compound forms when we add a precipitating reagent, or precipitant, to a solution that contains our analyte.In most cases the precipitate is the product of a simple metathesis reaction between the analyte and the precipitant; however, any reaction that generates a precipitate potentially can serve as a gravimetric .
Thermogravimetry. One method for determining the products of a thermal decomposition is to monitor the sample’s mass as a function of temperature, a process called thermogravimetry.Figure 8.3.1 shows a typical thermogram in which each change in mass—each “step” in the thermogram—represents the loss of a volatile product. As the following example . Definition. Gravimetric Analysis: Gravimetric analysis is a process of measuring the amount of an analyte by its mass. Volumetric Analysis: Volumetric analysis is a process used to determine the amount of a desired .Thermogravimetric analysis or thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) is a method of thermal analysis in which the mass of a sample is measured over time as the temperature changes. This measurement provides information about physical phenomena, such as phase transitions, absorption, adsorption and desorption; as well as chemical phenomena including .Adsorption refers to the process of adhesion of molecules or ions to a solid surface. It is the phenomenon where substances from a fluid phase, such as gases or liquids, accumulate on the surface of a solid material.
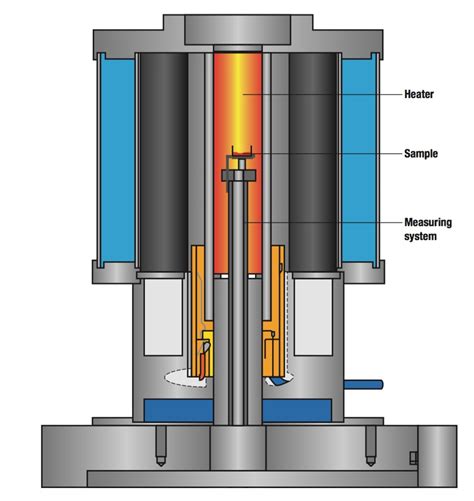
The definition of water activity is based on the concept of thermodynamics and refers to the availability of moisture in . The static gravimetric method involving the use of saturated salt solutions was applied successfully to the determination of . Adsorption EMC of hydroxypropylated cassava starch showing variation of MSI with temperature
what is the gravimetric method
CO 2 desorption performance in MDEA and MDEA + DEA rich amine solutions were studied with thermo-gravimetric analysis.. CO 2 desorption kinetics parameters were determined with thermal dynamic analysis method.. Desorption reaction rate constant for both MDEA and MDEA + DEA rich amine solutions were aquired. • The comparation of desorption performance . The availability of commercial gravimetric and volumetric systems for the measurement of adsorption equilibrium has seen also a growth of the use of these instruments to measure adsorption kinetics.
In most methods the precipitate is the product of a simple metathesis reaction between the analyte and the precipitant; however, any reaction generating a precipitate can potentially serve as a gravimetric method. Most precipitation gravimetric methods were developed in the nineteenth century, or earlier, often for the analysis of ores. Figure . In this paper, we propose a comparative study between a volumetric apparatus and a gravimetric one, which were developed for the acquisition of high-pressure adsorption isotherms. The volumetric apparatus is able to perform measurements in the temperature range 278?323 K and in the pressure range 0?4000 kPa. We provide a complete report on the .Method 4500-SO 4 2– C and Method 4500-SO 4 2– D as published in Standard Methods for the Examination of Waters and Wastewaters, 20th Ed., American Public Health Association: Washington, D. C., 1998. Jungreis, E. Spot Test Analysis; 2nd Ed., Wiley: New York, 1997.
In this paper, we propose a comparative study between a volumetric apparatus and a gravimetric one, which were developed for the acquisition of high-pressure adsorption isotherms. The volumetric apparatus is able to perform measurements in the temperature range 278–323 K and in the pressure range 0–4000 kPa. We provide a complete report on the experimental errors .
adsorption kinetics of pharmaceutical solids: A review . of the anhydrous forms and the hydrate were investigated by X-ray diffraction and the weight increase or decrease by a gravimetric method . Gravimetric analysis is an analytical technique used for the quantitative determination of an analyte based on the mass of solid.The element to be identified is precipitated from a solution using this method of analysis by the addition of a suitable precipitating agent.hydrogen gravimetric capacities measured at different laboratories, sample masses, and at 77 K and ambient temperature was shown. Overall, in the literature, t hese previous efforts have led to a more uniform reporting of gravimetric capacities. With respect to sorbent materials , adsorption is defined in

2018 fastpitch bat compression test
Resultado da 27 de out. de 2023 · Appyn Theme for Android Apps Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Integer fermentum erat ut massa .
gravimetric adsorption method definition|different types of gravimetric methods